1) Type 1 Diabetes
The body does not produce insulin. Some people may refer to this type as insulin-dependent diabetes, juvenile diabetes, or early-onset diabetes (Diabetes). People usually develop type 1 diabetes before their 40th year, often in early adulthood or teenage years
Type 1 diabetes is nowhere near as common as type 2 diabetes.
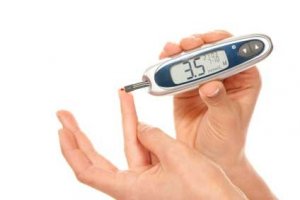
Patients with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin injections for the rest of their life. They must also ensure proper blood-glucose levels by carrying out regular blood tests and following a special diet. Between 2001 and 2009, the prevalence of type 1 diabetes among the under 20s in the USA rose 23% (Diabetes).
2) Type 2 Diabetes
The body does not produce enough insulin for proper function, or the cells in the body do not react to insulin (insulin resistance).
Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels (Bentley). However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.
• Overweight and obese people have a much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those with a healthy body weight. Being overweight/obese causes the body to release chemicals that can destabilize the body's cardiovascular and metabolic system (Youth Diabetes).
• Being overweight, physically inactive and eating the wrong foods all contribute to our risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is also greater as we get older. Experts are not completely sure why, but say that as we age we tend to put on weight and become less physically active.
 Post title...
Post title...
 Post title...
Post title...
 amberjm21
amberjm21