3) Gestational Diabetes
This type affects females during pregnancy. Some women have very high levels of glucose in their blood, and their bodies are unable to produce enough insulin to transport all of the glucose into their cells, resulting in progressively rising levels of glucose (Diabetes).
Diagnosis of gestational diabetes is made during pregnancy.
The majority of gestational diabetes patients can control their diabetes with exercise and diet. Between 10% and 20% of them will need to take some kind of blood-glucose-controlling medications. Undiagnosed or uncontrolled gestational diabetes can raise the risk of complications during childbirth (Bentley). The baby may be bigger than he/she should be.
How to Determine Whether You Have Diabetes, Pre-diabetes or Neither
Doctors can determine whether a patient has a normal metabolism, pre-diabetes or diabetes in one of three different ways - there are three possible tests:
The A1C test
- at least 6.5% means diabetes
- between 5.7% and 5.99% means pre-diabetes
- less than 5.7% means normal (Williams Textbook of
Endocrinology)
The FPG (fasting plasma glucose) test
- at least 126 mg/dl means diabetes
- between 100 mg/dl and 125.99 mg/dl means pre-diabetes
- less than 100 mg/dl means normal (Williams Textbook of Endocrinology)
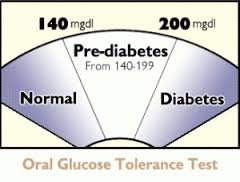
The OGTT (oral glucose tolerance test)
- at least 200 mg/dl means diabetes
- between 140 and 199.9 mg/dl means pre-diabetes
- less than 140 mg/dl means normal (Williams Textbook of Endocrinology)
 Post title...
Post title...
 Post title...
Post title...
 amberjm21
amberjm21