Exams and Tests
Asthma is generally determined by observation during a physical examination, medical history and family allergic disease. Laboratory tests and x-rays studies may eliminate identification of other diseases. The doctor or nurse will use a stethoscope to listen to your lungs. Wheezing or other asthma-related sounds may be heard (Asperen).
Tests that may be ordered include:
• Allergy testing - skin or a blood test to see if a person with asthma is
allergic to certain substances
• Arterial blood gas (usually only done is you’re having a
severe asthma attack)
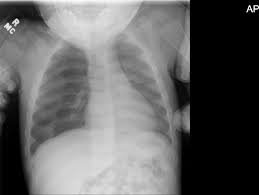
• Chest x-ray
• Lung function tests, including peak flow measurements (Nowak RM).
An attack may begin gradually or abruptly and is often preceded by an upper respiratory infection. Typically an attack begins with signs of air hunger; yawning; sighing; shortness of breath; wheezing; hacking, and a productive cough (Mayo Clinic Staff).
Management of asthma in children is based on four stages of severity: intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent. Intermittent asthma include symptoms that occur less than once a week, brief exacerbations from a few hours to a few days, night-time episodes that occur less than twice a month, and normal lung function between exacerbations. Mild persistent is characterized by symptoms that occur more than once a week, but less than once a day and night-time episodes that occur more often than twice a month. Moderate persistent severity is manifested by daily symptoms with exacerbations that affect daily activities and sleep. Sever persistent is characterized by continuous symptoms that limit physical activities, frequent exacerbations and night-time episodes (Asperen).
Treatment
The goals of treatment are:
• Control airway swelling.
• Stay away from substances that trigger your symptoms.
• Help you to be able to do normal activities without
asthma symptoms.
You and your doctor should work as a team to manage
your asthma. Follow your doctor's instructions on taking
medicines, eliminating asthma triggers, and monitoring symptoms (Nowak RM).
 Post title...
Post title...
 Post title...
Post title...
 amberjm21
amberjm21